Infineon, Littelfuse, and Toshiba Release High-Performance Power MOSFETs
Today's MOSFET innovations respond to the demand for high-power devices, efficient power supplies, and widespread electrification. Today we look at news in the MOSFET industry from Infineon, Littelfuse, and Toshiba that respond to the strict power requirements of these applications.

Infineon Brings Low RDS(on) and Linear Operation to Hot-Swappable MOSFETs
Infineon designed its new OptiMOS Linear FET 2 MOSFET with a cross-over construction architecture to improve performance in battery-powered, high-current devices.
The company claims the MOSFET (datasheet linked) excels in both high-current and hot-swapping applications. Hot swapping brings additional requirements to power MOSFETs. Such parts must have a low drain/source resistance when conducting (RDS(on)) and a robust linear operating mode. Infineon's MOSFET seems to meet this goal by trading off between the low RDS(on) typical of a trench MOSFET and the large safe operating area (SOA) of a more conventional planar MOSFET. The linear operation helps to limit hot swap inrush current that would otherwise be exaggerated due to the low RDS(on).
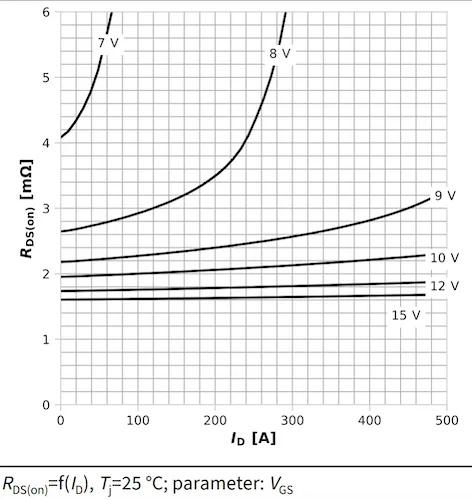
The typical drain‑source on-resistance of the OptiMOS Linear FET 2 MOSFET. Image used courtesy of Infineon
The new MOSFET operates at up to 100 V and 243 A and as low as 2.3 mΩ RDS(on). Compared to a standard OptiMOS 5 with a similar RDS(on), this gives the new MOSFET a 12 times higher SOA (54 V at 10 ms) and 3.5 times higher SOA at 100 µs.
The large SOA improves short circuit protection and current sharing attributes, resulting in up to 60% fewer components, according to Infineon. Infineon believes this low component count and high reliability make this MOSFET a useful option in e-bikes, power tools, forklifts, battery backup units, and battery-powered vehicles.
Littelfuse's High-Current MOSFETs Combine Parallel Parts Into One
Littelfuse has announced a pair of high-performance Ultra Junction X4-Class 200-V power MOSFETs. Littelfuse claims the IXTN400N20X4 and IXTN500N20X4 have industry-leading on-state resistance targeted at battery and power supply applications.
The new parts add to the company's existing 200-V Ultra Junction X4-class MOSFET product line. The two MOSFETs have RDS(on) values of 1.99 mΩ for the IXTN400N20X4 and 3 mΩ for the IXTN500N20X4. Compared to the existing X4-Class MOSFET solutions, the new parts offer up to double the current ratings and up to ~63% lower RDS(on) values.
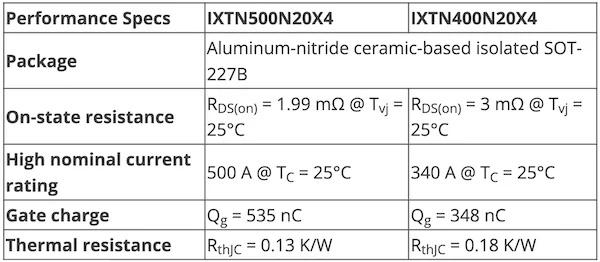
Key specifications for Littelfuse's IXTN400N20X4 and IXTN500N20X4 MOSFETs. Table used courtesy of Littelfuse
The current capability of these two parts comes in both the silicon and the packaging. The screw-mount terminal SOT-227B package has superior thermal properties. The high current capacity and low resistance allow single parts to replace multiple lower-current parallel MOSFETs in a power circuit design. Putting multiple parts into one reduces cost and design time and can lead to a more robust product. Littelfuse expects the MOSFETs to go into battery products such as storage, chargers, load switches, and power supplies.
Toshiba Leverages New Design Architecture for SiC MOSFETs
Toshiba recently introduced an automotive-targeted, low-RDS, bare-die SiC MOSFET. The AEC-100-qualified component delivers high reliability for traction inverters. The part has a drain-source voltage rating of 1,200 V and a drain-source current rating of 229 A. It delivers an RDS(on) of 7.2 mΩ at 25°C and 12.1 mΩ at 175°C.
Power MOSFET circuits, including electric vehicle inverter circuits, require a reverse Schottky barrier diode (SBD) to protect against flyback current. A built-in reverse body diode is an artifact of basic MOSFET design. However, the body diode is neither robust nor fast enough to adequately protect the transistor. Instead, the body diode can lead to less efficient operation. RDS(on) increases when the body diode is energized during reverse current operation, reducing reliability and efficiency. Silicon carbide (SiC) MOSFETs suffer more from this condition due to their typical high-power operating regimes.
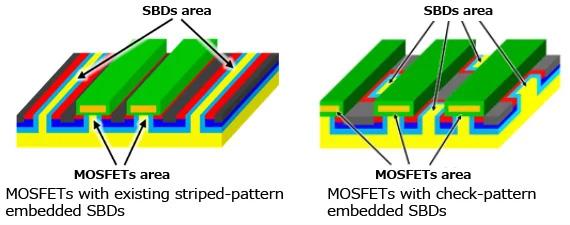
Conventional striped SDB (left) and new check-pattern SBD (right) with improved RDS(on) performance. Image used courtesy of Toshiba
Toshiba uses a novel design approach to mitigate the problem and deliver reliability and low RDS(on). The SiC MOSFETs integrate the SBD so that it does not conduct current during reverse operation. The new bare-die X5M007E120 MOSFET uses a check-pattern SBD architecture, allowing the MOSFET to operate without conducting during reverse regimes. The architecture fully allows the external SBD to take the reverse current load and prevents a rise in RDS(on) rating.
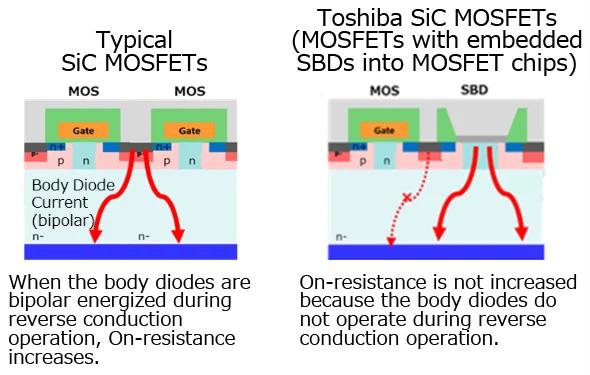
Conventional striped SDB (left) conducts during reverse operation and reduces efficiency. The new check-pattern SBD (right) does not energize the body diode. Image used courtesy of Toshiba
The new MOSFET promises to improve short-circuit performance and reduce leakage current. By offering the part in bare-die form, circuit designers have the most flexibility for integrating the device into maximum-performance designs.
MOSFET Improvement Marches On
Despite a growing fascination with AI processors and wireless protocols, the MOSFET remains the foundation of many critical power technologies. These three new components from Infineon, Littelfuse, and Toshiba will find homes in designs from electric cars and charging stations to backup power systems that require high performance from electronic switching systems. Each contains design innovations showing that the cycle of MOSFET improvement is still going strong.
Sign up to our newsletter
Receive our latest updates about our products & promotions
